 Linux file server is one of the powerful servers that helps you to share files and printers with Windows-based PCs and other operating systems. Before we talk about using Samba as a file server, let’s discuss some basics. To understand Linux/Samba/Windows relationship, you need to understand the relationships of the operating systems, users, and networks. Linux login system is different from the Windows login system. So, it’s the system administrator job to maintain the logins between different platforms. There are several solutions to do this: Linux pluggable authentication modules (PAMs): there are two user lists, one local list and one on the domain controller (DC), and users need to maintain their passwords only on the Windows system.
Linux file server is one of the powerful servers that helps you to share files and printers with Windows-based PCs and other operating systems. Before we talk about using Samba as a file server, let’s discuss some basics. To understand Linux/Samba/Windows relationship, you need to understand the relationships of the operating systems, users, and networks. Linux login system is different from the Windows login system. So, it’s the system administrator job to maintain the logins between different platforms. There are several solutions to do this: Linux pluggable authentication modules (PAMs): there are two user lists, one local list and one on the domain controller (DC), and users need to maintain their passwords only on the Windows system.
Linux/Samba/Windows Relationship
- Samba as a DC: you maintain usernames and passwords on the Linux system, and users can log in to Windows boxes with Samba
- Custom script: you can create scripts for maintaining logins and passwords, this can be done using a cross-platform scripting language like python.
The samba server composed of several components and daemons, the three main daemons are smbd, nmbd, and winbindd.
- The smbd daemon is the main service for the sharing of files and printers. This daemon uses port 139 or 445 to listen for requests.
- The nmbd daemon handles NetBIOS name service requests. This daemon uses port 137 to listen for requests.
- The winbindd is used to get user and group information from Windows.
Install Samba
To install Linux file server, you need to install three packages.
For Red Hat based distros, you can install them like this:
dnf -y install samba
This package installs SMB server.
dnf -y install samba-common-tools
This package includes the required files for both the server and client.
dnf -y install samba-client
For Debian based distros, you can install them like this:
apt-get -y install samba
apt-get -y install samba-common-tools
apt-get -y install samba-client
Then you can start samba service and enable it at startup:
systemctl start smb
systemctl enable smb
Samba File Sharing
Of course, you can use web-based or GUI utilities to manage your Linux file server. However, it is useful to understand what GUI or web tools are doing from behind.
Now we will share a folder named myfolder:
chmod -R 755 myfolder
Open up Samba configuration file /etc/samba/smb.conf and add the following lines at the end:
[likegeeks]
path=/home/likegeeks/Desktop/myfolder
public=yes
writable=no
guest ok=yes
The first line is the Samba server name that the clients see.
The second line is the path to the folder that will be shared.
The third line means the share will available to all users like guest account and others. If set to no, authenticated and permitted users are only allowed.
The fourth line means that you cannot create or modify the stored files on the shared folder.
You can check for SMB configuration errors using the testparm command:
testparm
Now restart SMB service:
systemctl restart smb
Now we need to access what we’ve shared. The smbclient utility is used to access Windows shared files.
You can list the shared files like this:
smbclient -L localhost -U%
The -U% option is used to avoid asking for the password.
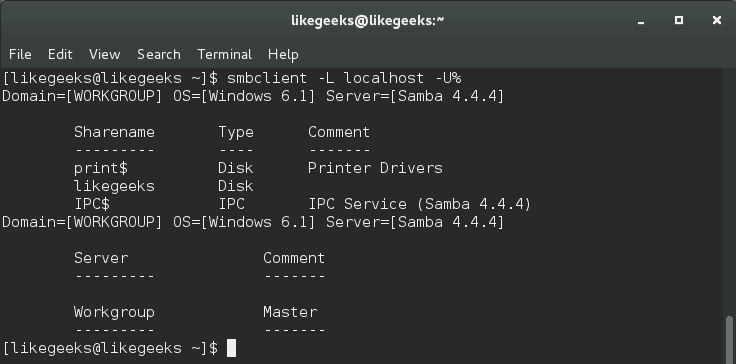
As you can see our shared folder is on the list.
You can access this shared folder from Windows by just typing the IP address in the Windows explorer.
\\192.168.1.3\
You can list a specific directory using the smbclient tool like this:
smbclient -U% //192.168.1.2/My_Folder
Once you’ve connected, you can use Linux commands to list and travel between files.
You can transfer files using get, put, mget, and mput commands.
If you are using iptables firewall, don’t forget to allow the ports 137,139 and 445.
Most Linux kernels support SMB file system.
To mount a Samba share, First, create a mount point:
mkdir /mnt/smb
Then we mount the SMB shared folder:
mount -t cifs -o guest //192.168.1.2/My_Folder /mnt/smb
If the shared folder is password protected, then you type the username and password:
mount -t cifs username=likegeeks,password=mypassword //192.168.1.2/My_Folder
To unmount the SMB shared folder, use the unmount command like this:
umount /mnt/smb
On Debian based distros, you might need installing the cifsutils package in order to use it:
apt-get -y install cifs-utils
Creating Samba Users
To create a samba entry for an existing system user, use the pdbedit command:
pdbedit -a likegeeks
The new user will be created in the Samba default user database which is /var/lib/samba/private/passdb.tdb file.
With a Samba user created, we can make the shares available only to authenticated users like the user likegeeks.
This user can access his resources on Samba server using smbclient like this:
smbclient -U likegeeks -L //192.168.1.3
The smbpasswd command is used to change the SMB password like this:
smbpasswd likegeeks
Authenticate Users Using Windows Server
The winbindd daemon is used for resolving user accounts information from native Windows servers.
First, install the winbind package.
dnf -y install samba-winbind
Then start the service like this:
systemctl start winbind
Then add the following options in /etc/samba/smb.conf file:
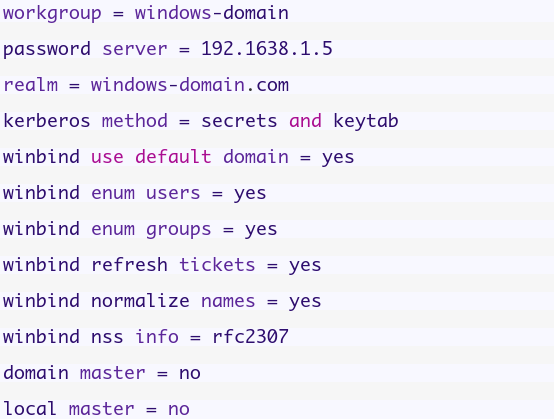
Then Edit the /etc/nsswitch.conf file and modify the following lines:
passwd: files winbind
shadow: files winbind
group: files winbind
Then Edit the /etc/resolv.conf file and change the primary DNS server:
Search windows-domain.com
nameserver 192.168.1.5
Now join the Linux Samba server from the Windows domain using the net command:
net join -w WINDOWS-DOMAIN -s ' win-server' -U Administrator%password
You can list the users in the Windows domain using wbinfo command
wbinfo -u
For any problem diagnostics, you can check the samba log files under /var/log/samba/ directory, also use testparm utility to check your configuration after you modify the samba configuration file.
That’s all. I hope you find the Linux file server easy. Keep coming back.
Thank you.


